Hemp likely originated in Central Asia. Cultivation for fibre was recorded in China as early as 2800 BCE and was practiced in Europe early in the Christian era, spreading throughout the entirety of Europe during the Middle Ages. Hemp made its way to Chile in the 1500’s and a century later in North America.
According to the United States Department of Agriculture, the agency that regulates hemp production, industrial hemp includes “the plant Cannabis sativa L. and any part or derivative of such plant, including seeds of such plant, whether growing or not, that is used exclusively for industrial purposes (fiber and seed) with a tetrahydrocannabinol concentration of not more than 0.3 percent on a dry weight basis.”
While Hemp and Cannabis both derive from the Cannabis Sativa family and do share certain similarities, due to each plant’s biological structure, they have several distinct and vital differences.

 FLOWERS
FLOWERS  SEEDS
SEEDS  FIBER/STALKS
FIBER/STALKS Hemp and Cannabis also posses crucial differences in their chemical composition. Cannabis contains a variety of different compounds called Cannabinoids, two of the most common are Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD).
Both Cannabinoids have shown to provide profound benefits to the human body; however, THC induces psychoactive effects (gets the user “high”), while CBD does not contain psychoactive properties. While Hemp does, in fact, contain a very low concentration of THC (0.3% or less), Cannabis is abundant in THC with concentrations between 15% to 40%. Because of this distinction, Hemp is grown primarily for industrial purposes, while Cannabis is grown for recreational and medicinal purposes.


CBD has been shown to counteract the psychoactive properties of THC. Additionally to CBD’s non-psychoactive properties, research has shown that it contains antioxidant and neuroprotection properties.
According to a 2013 study published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology:
CBD benefits including acting in some experimental models as an anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, antioxidant, antiemetic, anxiolytic and antipsychotic agent, and is, therefore, a potential medicine for the treatment of neuro-inflammation, epilepsy, oxidative injury, vomiting, and nausea, anxiety, and schizophrenia.

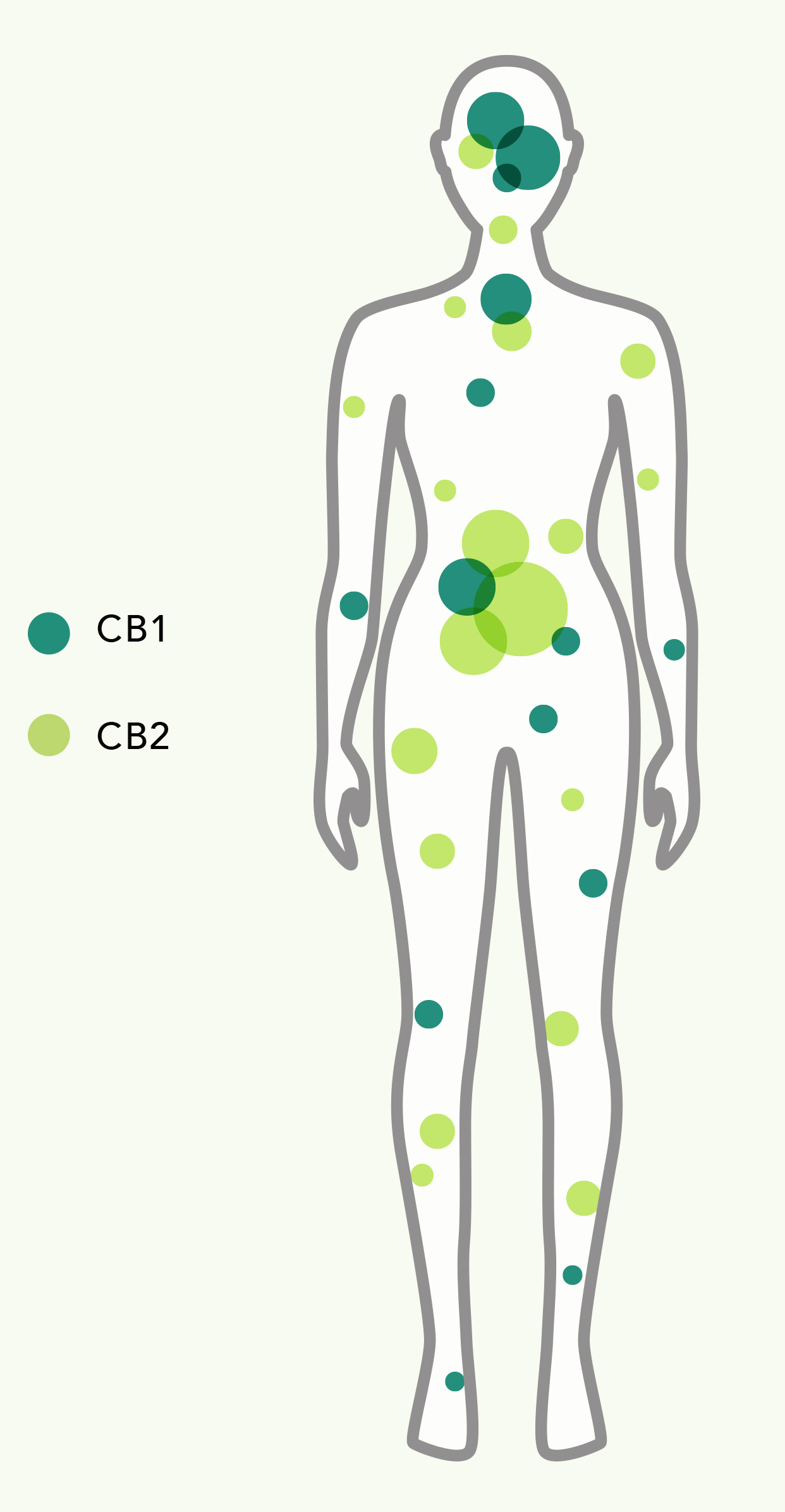
There are two primary receptors which are affected by cannabinoids: CB1 and CBD2 receptors. While cannabinoids possess similar structures, they also affect receptors very differently. Research has shown that THC helps to regulate the CBD1 and CBD2 receptors, resulting in psychoactive effects, while CBD has very little effect on these receptors.
Homeostasis is responsible for our inner balance, physiologically and even psychologically. It refers to the processes which our body employs to maintain a stable environment, even at times when we feel unstable and those processes are undesirable.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a network or a messenger system of hormones and neurotransmitters which permeates our bodies. Its two main components are the endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors which are spread throughout different areas of our bodies when homeostasis is disrupted, the ECS excretes endocannabinoids into our vessels and “sends” them to communicate with the cannabinoid receptors in the affected area of our body. Endocannabinoids signal the receptors to trigger the necessary responses which work to restore the equilibrium.
The ECS does this via cannabinoid receptors found in select tissues. We have (at least) two types of cannabinoid receptors:
CB1 which is in the central nervous system (brain and nerves of the spinal cord).CB2 which is in the peripheral nervous system (nerves in your extremities), the digestive system, and specialized cells in the immune system.
Motor activity
Thinking
Motor co-ordination
Appetite
Short term memory
Pain perception
Immune cells
Gut
Kidneys
Pancreas
Adipose tissue
Skeletal muscle
Bone
Eye
Tumours
Reproductive system
Immune system
Respiratory tract
Skin
CNS
Cardiovascular system
Liver



Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic molecules that are present in Cannabis and a wide variety of plants. Terpenes account for aromas and flavors produced by the essential oils of many types of plants. Terpenes generate distinct effects on the human body that vary among individuals. Additionally, terpenes work together with cannabinoids to produce an array of effects and therapeutic benefits known as the Entourage Effect.
The Entourage Effect is the synergetic effect stemming from various natural components within a plant that interact together with the human body to induce different, often intensified, effects.
